What is an STI assessment?
An assessment for sexually transmitted infections (STI screening) consists of:
- A brief sexual history
- Education
- A physical examination if necessary
- Possible laboratory testing
Your health care provider will determine with you what tests, if any, are appropriate. Tests may require:
- A urine sample
- Oral, vagina, penile or rectal swab
- Cervical culture and/or
- Blood draw
STI assessment can include HIV testing or HIV testing can be done separately and rapidly. See HIV Testing for more info.
STI assessments have limitations
It is not possible to test for all STIs. Talk to your health care provider about what tests can be performed.
When should I have an STI assessment?
An assessment is recommended for routine testing, if you have been (or may have been) exposed to an STI, or if you experience symptoms, such as:
- Unusual discharge
- Painful or burning with urination
- Genital skin changes (rash, sore, blister, growths)
- Pelvic discomfort or pain (women)
- Testicular pain (men).
Note: It's important to see a clinician when symptoms are present. However, a person who has an STI may not experience any symptoms and there may be other causes of these symptoms.
Routine Gynecological Health Exams are recommended annually. People who have a cervix may be recommended to have a Pap test.
People who are sexually active are advised to have an STI assessment, according to the recommendations above.
See the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's STI page for more information.
How can I get an STI assessment?
Call 734-764-8320 and ask about an STI assessment, or you may contact your health care provider through the patient portal (you will need an account).
When you call, you will be asked:
- Whether a partner has told you that they have an STI
- Whether you have any symptoms
You may then schedule an appointment at UHS or a nurse will call you back to assess your needs by phone and order lab tests. Please be sure that your phone voicemail is set up and your voicemail is not full.
Fees
- For currently enrolled U-M students and UHS Prepaid Plan members, there are no fees for the clinic visit or the most commonly tested for STIs:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Herpes
- HIV
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Syphilis
- Trichomonas
- For other patients, there are fees for clinic visits and lab testing.
- There are no fees for STI testing as part of the Sexual Assault Exam or as a result of sexual assault.
- See:
What about confidentiality?
- Your medical records are kept confidential and can be released ONLY with your written consent, however:
- UHS will bill diagnostic testing to your personal health insurance except for sensitive tests such as for STI testing for students. Services may appear on the insurance holder's Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statements if insurance is billed.
- As an alternative to billing insurance, the UHS Patient Billing Office can offer other payment options on the same day that your tests or services are ordered/performed. Payment must be made within 30 days.
How can I get test results?
Your health care provider will tell you how to get your test results. STI test results are typically available 2-3 business days after your visit. HIV test results usually take longer. You can get results through the Patient Portal (you will need an account).
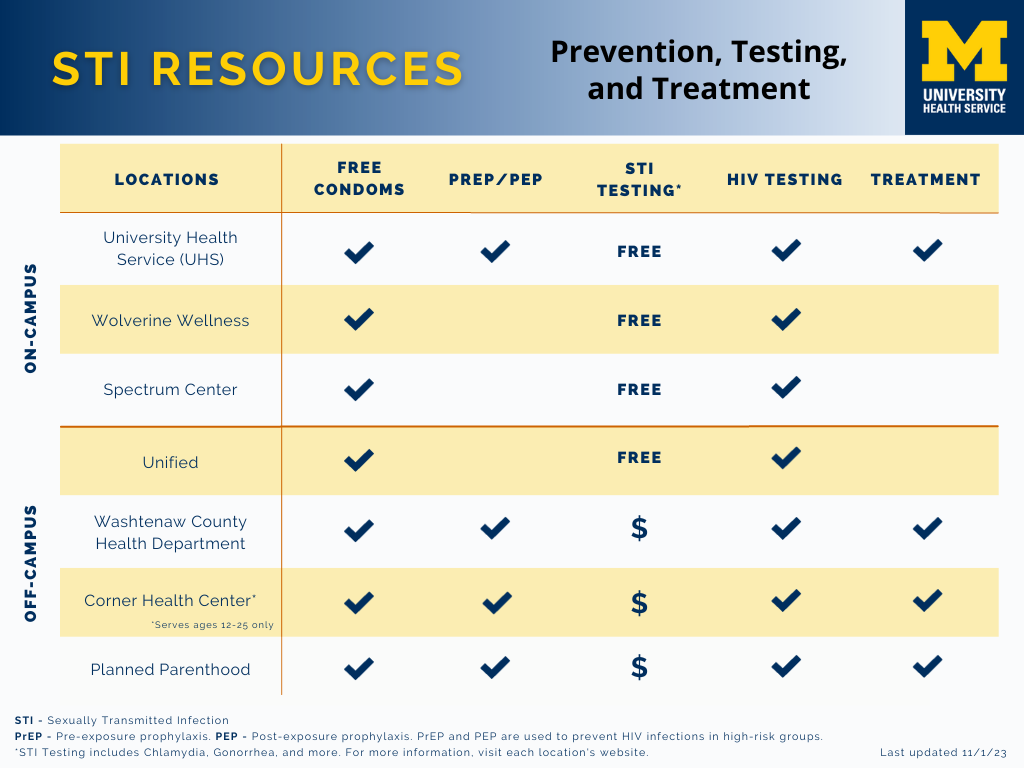
Other local clinics for STI testing
Low- or no-cost STI testing (depending on your income) is available at many locations in the community. See our STI Resource Guide for more details on each testing site.
Suggestions for STI/HIV prevention
- No partners (abstaining) or fewer partners generally means less risk.
- Decide with your partner(s) about how you will practice safer sex.
- Ask questions about your partners' sexual history, including STI assessment and HIV Testing.
- Choose lower risk sexual activities, such as mutual masturbation instead of intercourse.
- Use a condom (latex or polyisoprene) during intercourse. Use a silicone or water-based lubricant to reduce the risk of breakage.
- Use a barrier (condom, latex square, etc.) with oral-genital or oral-anal contact.
- Wash shared sex toys thoroughly between uses.
- Minimize damage to tissues during sexual activities by using adequate lubrication and avoiding behaviors that draw blood.
- Avoid mixing alcohol or other drugs with sex because they interfere with decision making, consent, and sexual performance.
Resources for sexual health information
- Reproductive Health
- Safer Sex Supplies
- Emergency Contraception
- HIV Testing
- Medications for HIV Prevention
- Pregnancy Testing
- STI Testing Resource Guide
- Common Myths and Misconceptions of STIs
- Glossary of STIs
- Sexual Health
- Resources for Sexual Health
- Sexual Health Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- How to Get Health Care at UHS - You can talk to a nurse by phone or meet with a clinician regarding any concerns.