What is the implant?
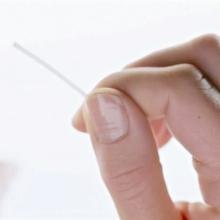
The implant (brand name Nexplanon®) is a small, flexible plastic rod about the size of a matchstick. It contains the progesterone-like hormone, etonogestrel, and is used to prevent pregnancy. The implant is a prescription form of contraception.
How does it work?
A health care provider places the implant under the skin of your upper arm, which takes only 1-2 minutes. Once inserted, the implant continuously releases a small amount of hormone into your body.
The hormone prevents pregnancy by: